Spenmo is a technical service provider that facilitates spend management and is not required to be licensed under the Payment Services Act 2019 of Singapore (“PS Act”). All payment services are provided by Spenmo’s partners (and not by Spenmo) , who are licensed major payment institutions under the PS Act.
Streamline Company Spend While Maintaining Control
Spenmo empowers you with enhanced visibility and control to automate your existing spend management processes.
Streamline Company Spend While Maintaining Control
Spenmo empowers you with enhanced visibility and control to automate your existing spend management processes.
Your Co-Pilot in Steering Spend Control
Efficiency and Cost-Saving
Smart automation with guardrails, drive productivity and uncover cost savings
Gain Flexibility and Control
Seamless claims processing with spend and budget controls
Eliminate Out-of-Policy Spend
Enhance visibility with real-time dashboard and customisable approval flow
Reduce Reconciliation Headaches
Seamless accounting integration reduces manual entry and errors
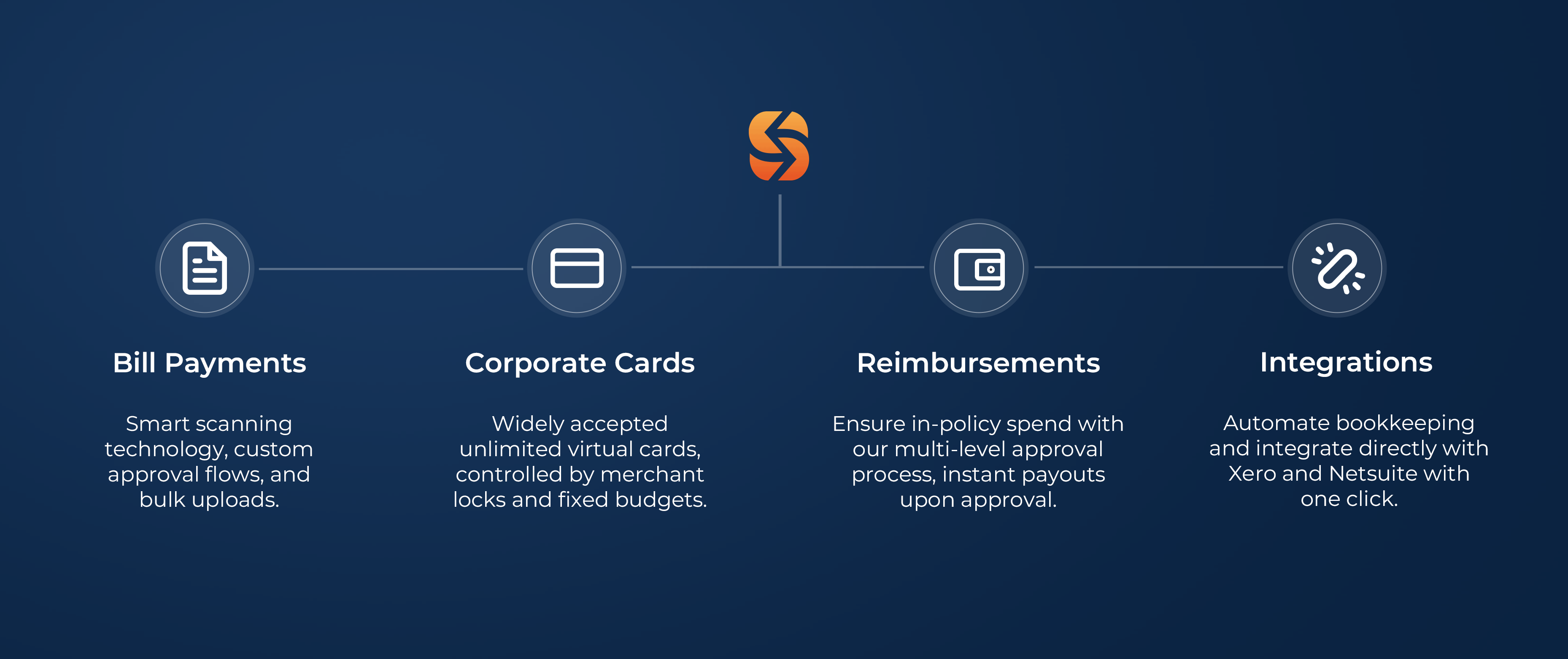








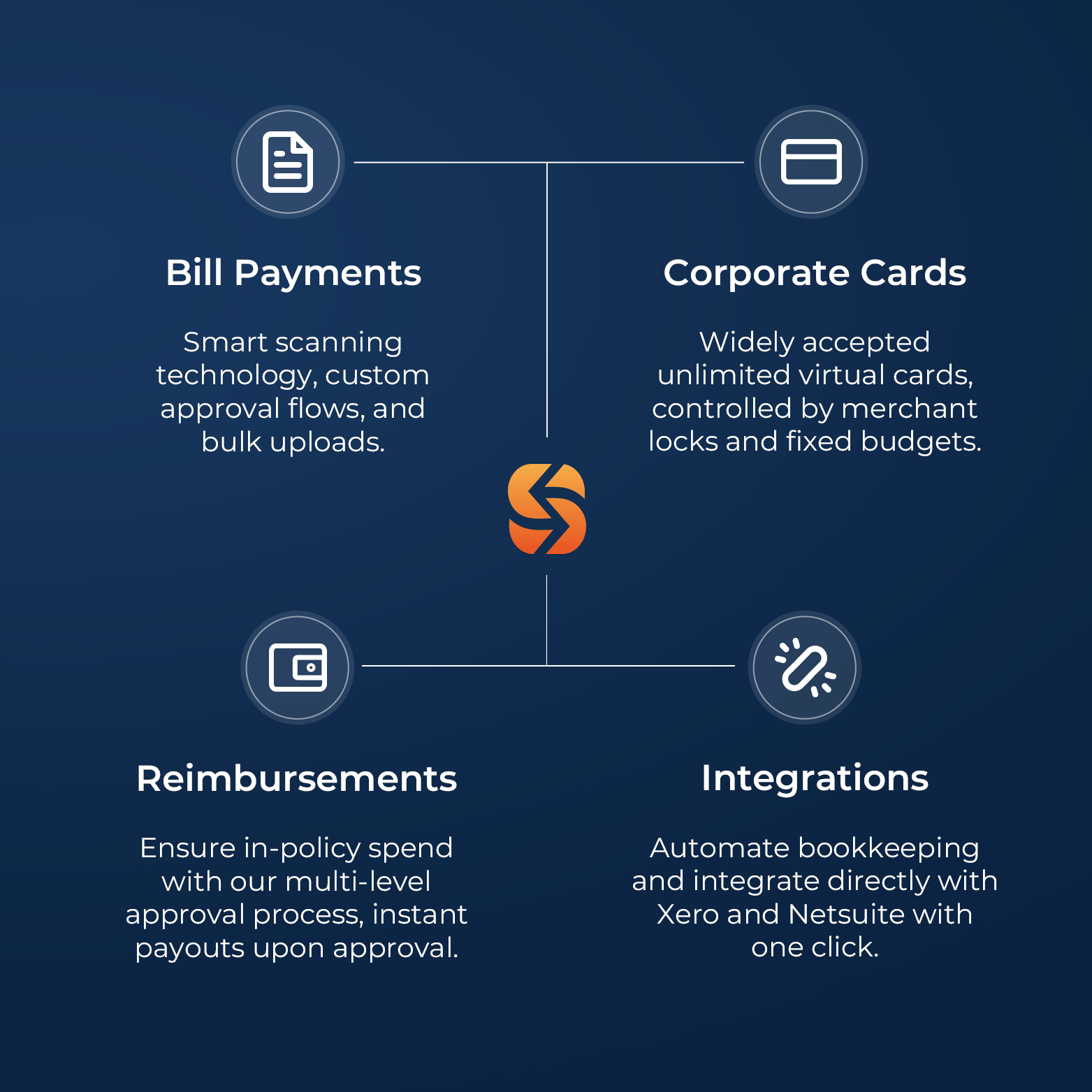








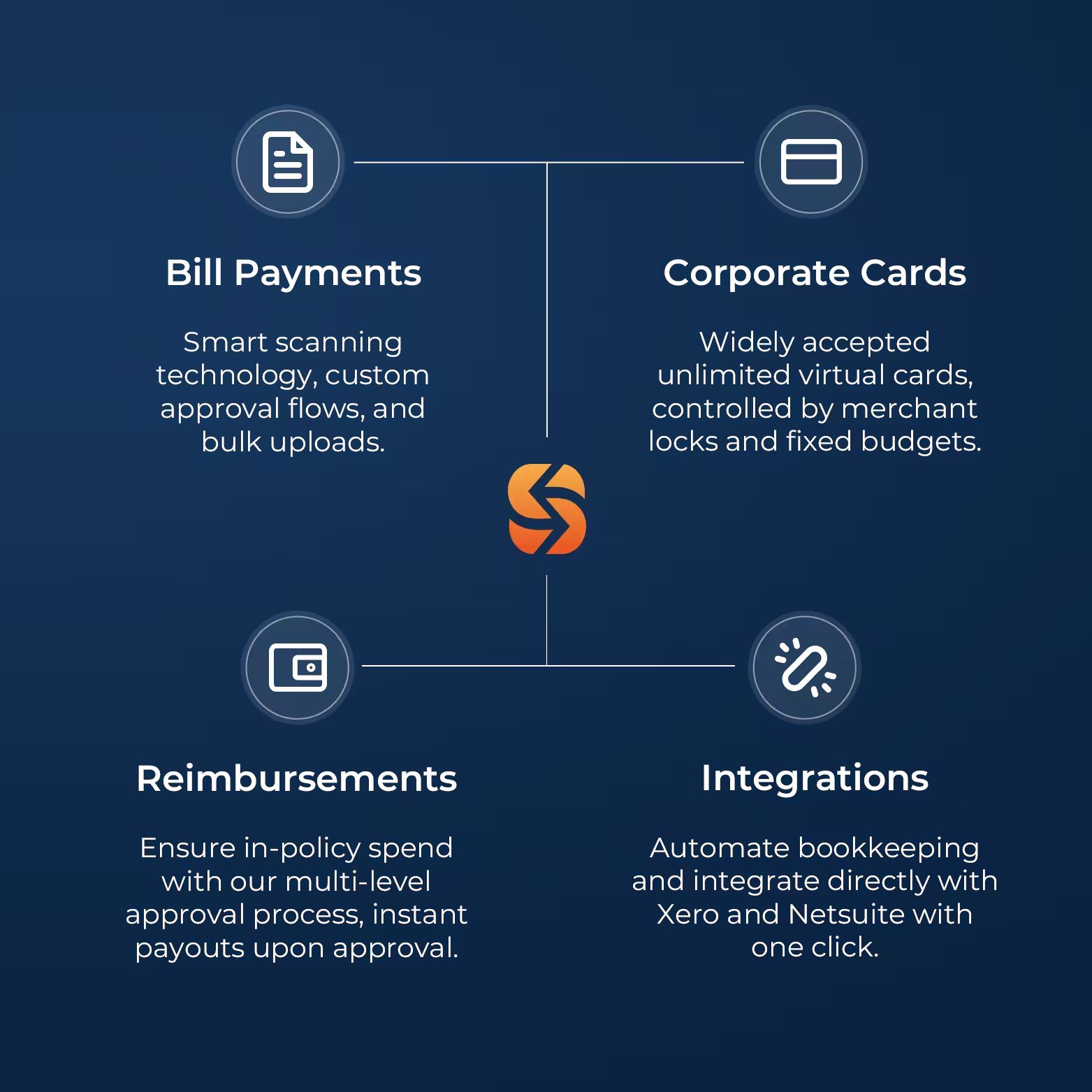

Bill Management
Process your bills up to 90% faster
Reduce manual effort and errors while maintaining full control with our Smart Scanning technology, accounting software integrations, and custom approval workflows.
Utilise domestic and cross-border payment services provided by Spenmo’s partner licensed payment service providers.

Bill Management
Process your bills up to 90% faster
Reduce manual effort and errors while maintaining full control with our Smart Scanning technology, accounting software integrations, and custom approval workflows.
Utilise domestic and cross-border payment services provided by Spenmo’s partner licensed payment service providers.

Corporate Debit Card
Access to Visa Debit Cards
Gain access and control to physical and virtual Corporate Debit Cards issued and processed by Spenmo’s partner licensed payment service provider to make reimbursements and out-of-policy spending a hassle-free accounting experience!
-4.gif?width=991&height=731&name=reimbursements%20gif%20(1)-4.gif)
Reimbursements
Enhanced visibility, reduce petty cash spend by 30%1
Disburse claims in a few clicks via our licensed payments partner while ensuring in-policy spending with our multi-level approval process.
1 based on internal customer interview
-4.gif?width=991&height=731&name=reimbursements%20gif%20(1)-4.gif)
Reimbursements
Enhanced visibility, reduce petty cash spend by 30%1
Disburse claims in a few clicks via our licensed payments partner while ensuring in-policy spending with our multi-level approval process.
1 based on internal customer interview
Corporate Debit Card
Access to Visa Debit Cards
Gain access and control to physical and virtual Corporate Debit Cards issued and processed by Spenmo’s partner licensed payment service provider to make reimbursements and out-of-policy spending a hassle-free accounting experience!

Accounting Software Integration
Close books up to 70% faster
Syncs seamlessly with Xero, Netsuite, Quickbooks, Jurnal, and more, ensuring faster reconciliation and accurate data.


Seamless Accounting Software Integration
Close books up to 70% faster
Syncs seamlessly with Xero, Netsuite, Quickbooks, Jurnal, and more, ensuring faster reconciliation and accurate data.
ISO 27001 Certified
Spenmo's ISO 27001 certification signifies rigorous adherence to global information security standards, assuring clients that their data is meticulously safeguarded against potential threats.